What is Kubernetes Pod QoS?
Container orchestration, Kubernetes has emerged as a leading platform for managing and deploying containerized applications. One fundamental concept that plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance is the Quality of Service (QoS). In the realm of Kubernetes, this concept is applied at the level of Pods, forming the backbone of resource management within the cluster.
What is a Kubernetes Pod?
Before delving into QoS, it’s essential to grasp the basic unit of deployment in Kubernetes—the Pod. A Pod represents the smallest deployable unit in the Kubernetes ecosystem, encapsulating one or more containers that share the same network namespace, storage, and have the potential for inter-container communication.
What is Kubernetes Pod QoS
Quality of Service (QoS) in Kubernetes refers to the system’s ability to prioritize and manage resources effectively among different pods running within the cluster. Kubernetes offers three levels of QoS for pods: BestEffort, Burstable, and Guaranteed. These QoS classes determine how Kubernetes schedules and allocates resources to pods based on their resource requirements and usage patterns.
Managing Pod QoS
To effectively manage Pod QoS in Kubernetes, consider the following best practices:
-
Resource Allocation: Analyze your application’s resource requirements and allocate resources accordingly by specifying resource requests and limits in your pod manifest files.
-
Monitoring and Scaling: Monitor your cluster’s resource utilization using tools like Prometheus and Grafana. Implement autoscaling to dynamically adjust the number of replicas based on resource usage patterns and demand.
-
Tuning QoS Classes: Understand the characteristics of each QoS class and assign appropriate QoS classes to your pods based on their criticality and resource requirements.
-
Pod Disruption Budgets (PDB): Define Pod Disruption Budgets to control the impact of pod evictions during maintenance or resource contention scenarios, ensuring the availability and stability of your applications.
-
Testing and Optimization: Regularly test and optimize your application’s resource utilization to identify inefficiencies and fine-tune resource requests and limits for optimal performance.
Understanding Quality of Service (QoS):
Quality of Service, in the context of Kubernetes Pods, refers to the guarantee or priority given to Pods in terms of resource allocation. Kubernetes distinguishes between three QoS classes: Guaranteed, Burstable, and BestEffort.
-
Guaranteed QoS: Pods with guaranteed QoS have specified resource requests and limits.Kubernetes ensures that the specified resources are always available for these Pods.These Pods are suitable for critical workloads where resource consistency is paramount.
-
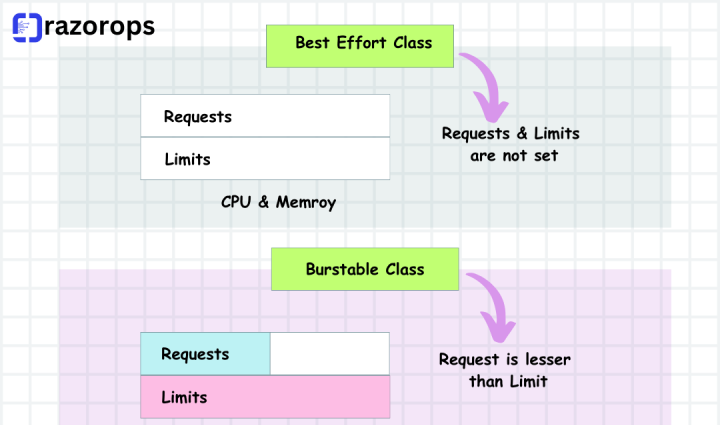
Burstable QoS: Pods falling under the burstable QoS class have resource requests and limits, but with the possibility of utilizing additional resources when available.Kubernetes allows these Pods to consume extra resources during periods of low cluster activity.Ideal for workloads with fluctuating resource demands.
-
BestEffort QoS: Pods in the BestEffort class have no specified resource requests or limits.These Pods are the lowest priority, and Kubernetes allocates resources based on availability.Suitable for non-critical workloads where resource constraints are acceptable.
Why does QoS matter?
Resource Efficiency:
-
QoS ensures efficient use of cluster resources by prioritizing and allocating them based on workload requirements.
-
Prevents resource contention and ensures a smooth operation of applications.
Performance Optimization:
-
Pods with guaranteed QoS receive consistent resources, optimizing the performance of critical applications.
-
Burstable QoS allows for flexibility, enabling applications to scale resources based on demand.
Cluster Stability:
- By categorizing Pods into different QoS classes, Kubernetes maintains cluster stability and prevents any single Pod from monopolizing resources.
Best Practices for Managing Pod QoS
To make the most of Kubernetes Pod QoS, consider the following best practices:
-
Set Resource Requests and Limits: Always define resource requests and limits for your Pods based on their resource requirements and expected usage patterns.
-
Use Horizontal Pod Autoscaling (HPA): Implement Horizontal Pod Autoscaling to automatically adjust the number of replicas for your workloads based on resource utilization, helping maintain optimal performance and resource allocation.
-
Monitor and Tune: Continuously monitor resource utilization and performance metrics for your Pods and adjust resource requests and limits as needed to optimize performance and prevent bottlenecks.
-
Review Eviction Policies: Understand the eviction policies configured in your Kubernetes cluster and ensure they align with your application’s requirements and SLAs.
In the intricate landscape of Kubernetes, understanding and implementing Quality of Service for Pods is crucial for achieving optimal performance, resource efficiency, and maintaining the stability of your containerized applications. Whether you’re running critical workloads that demand consistency or flexible applications with varying resource needs, Kubernetes QoS provides the framework to manage and allocate resources effectively within your cluster. Follow RazorOps Linkedin Page Razorops, Inc.
Enjoyed this article? Share it.







