Testing and Quality Assurance Within a CI/CD Pipeline

Testing and Quality Assurance Within a CI/CD Pipeline: A Detailed Guide
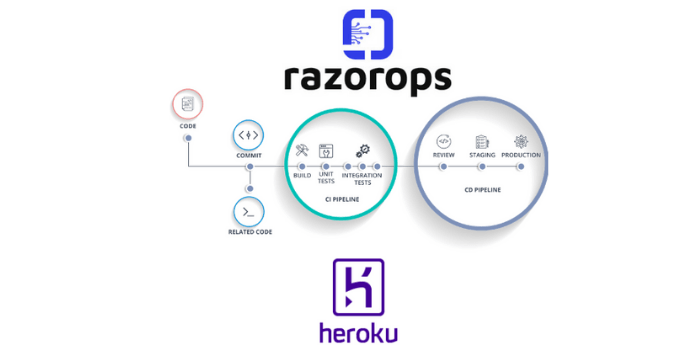
In today’s fast-paced software development landscape, the need to deliver high-quality software rapidly and reliably is paramount. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery/Deployment (CD) have emerged as essential practices that enable development teams to meet these demands. Central to the success of CI/CD pipelines is a robust framework for testing and quality assurance (QA). This blog post provides a comprehensive overview of how testing and QA integrate within CI/CD pipelines, ensuring the delivery of reliable, secure, and high-performing software.
The Importance of Testing and QA in CI/CD
Testing and QA are critical components of CI/CD pipelines. They ensure that code changes do not introduce new bugs, maintain software quality, and meet performance, security, and compliance requirements. Integrating automated testing and continuous QA processes into CI/CD pipelines offers several key benefits:
- Early Detection of Issues: Automated tests run continuously, catching bugs and issues early in the development cycle.
- Continuous Feedback: Developers receive immediate feedback on code quality, enabling rapid iteration and improvement.
- Reduced Risk: Continuous testing reduces the risk of defects reaching production, ensuring a stable and reliable software product.
- Faster Delivery: Automation speeds up the testing process, allowing for more frequent and reliable releases.
Types of Testing in CI/CD Pipelines
A comprehensive CI/CD pipeline incorporates various types of testing to validate all aspects of the software. Here are the primary types of testing involved:
1. Unit Testing
Purpose: Validate individual components or functions of the codebase to ensure they work as intended.
Characteristics:
- Fast and lightweight.
- Typically written and run by developers.
- High test coverage is desirable.
Tools: JUnit (Java), NUnit (.NET), pytest (Python).
2. Integration Testing
Purpose: Verify that different modules or services within the application work together correctly.
Characteristics:
- Test interactions between components.
- May involve databases, APIs, or other external systems.
- Often more complex and slower than unit tests.
Tools: TestNG (Java), pytest (Python), JUnit (Java).
3. Functional Testing
Purpose: Evaluate the application against its functional requirements to ensure it behaves as expected.
Characteristics:
- Test the end-to-end functionality of the application.
- Focus on user scenarios and workflows.
- Often automated using tools that simulate user interactions.
Tools: Selenium, Cypress, QTP/UFT.
4. Regression Testing
Purpose: Ensure that new code changes do not adversely affect existing functionality.
Characteristics:
- Re-run existing tests to verify previously working functionality.
- Helps prevent the introduction of new bugs.
Tools: Any test automation framework with good test suite management.
5. Performance Testing
Purpose: Measure the application’s performance under various conditions to ensure it meets performance criteria.
Characteristics:
- Includes load testing, stress testing, and scalability testing.
- Identifies performance bottlenecks and ensures the application can handle expected traffic.
Tools: JMeter, LoadRunner, Gatling.
6. Security Testing
Purpose: Identify vulnerabilities and ensure that the application is secure against attacks.
Characteristics:
- Includes static and dynamic analysis, penetration testing, and vulnerability scanning.
- Ensures compliance with security standards and regulations.
Tools: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, SonarQube.
7. Acceptance Testing
Purpose: Validate the application against business requirements and ensure it meets the needs of stakeholders.
Characteristics:
- Often involves manual testing by QA teams or end-users.
- Can include automated acceptance tests for repetitive scenarios.
Tools: Cucumber, FitNesse, Robot Framework.
Best Practices for Testing and QA in CI/CD
Implementing effective testing and QA practices within CI/CD pipelines requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider:
1. Shift-Left Testing
Shift-left testing involves moving testing activities earlier in the development process. By integrating testing into the CI/CD pipeline from the start, issues can be identified and resolved sooner, reducing the cost and impact of defects.
2. Automate as Much as Possible
Automating tests ensures consistency and reliability. Automated tests can be run frequently and consistently, providing continuous feedback to developers. Prioritize automation for repetitive and critical tests, such as unit, integration, and regression tests.
3. Maintain Test Independence
Ensure that tests are independent and can run in isolation. This reduces the risk of cascading failures and makes it easier to identify the root cause of issues.
4. Use Mocking and Stubbing
Use mocks and stubs to simulate external dependencies and isolate the system under test. This approach makes tests more reliable and faster by avoiding the need to set up complex environments.
5. Monitor and Measure Test Effectiveness
Continuously monitor test results and measure the effectiveness of your tests. Track metrics such as test coverage, test execution time, and defect detection rates to identify areas for improvement.
6. Implement Robust CI/CD Pipelines
Design your CI/CD pipelines to handle different types of tests efficiently. Use parallel execution and resource management to optimize test performance and reduce bottlenecks.
7. Foster a Culture of Quality
Encourage a culture of quality within the development team. Promote collaboration between developers, QA engineers, and operations teams to ensure that everyone is committed to delivering high-quality software.
Tools and Technologies for Testing and QA in CI/CD
There are numerous tools and technologies available to support testing and QA within CI/CD pipelines. Some popular options include:
- CI/CD Platforms: Jenkins, RazorOps CICD
- Test Automation Frameworks: Selenium, Cypress, JUnit, TestNG, pytest.
- Performance Testing Tools: JMeter, LoadRunner, Gatling.
- Security Testing Tools: OWASP ZAP, Burp Suite, SonarQube.
- Monitoring and Reporting Tools: Allure, TestRail, Grafana.
Conclusion
Testing and quality assurance are fundamental to the success of CI/CD practices. By integrating comprehensive testing strategies into CI/CD pipelines, development teams can ensure that their software is reliable, secure, and meets the needs of users and stakeholders. Embracing best practices and leveraging the right tools and technologies will lead to more efficient development processes, faster delivery cycles, and ultimately, higher-quality software products.
Incorporating these practices into your CI/CD pipeline will not only improve the quality of your software but also enhance team collaboration, accelerate delivery, and drive innovation. As the software development landscape continues to evolve, a robust testing and QA framework within your CI/CD pipeline will be critical to staying competitive and delivering exceptional value to your users.