Introduction to Helm 3 the Package Manager for Kubernetes

Helm is the package manager for Kubernetes (like yum, apt and home brew ) that allows easily package, configure, and deploy applications onto Kubernetes clusters.
Helm charts are packages (like debs and rpms) It contains pre-configured kubernetes resources such as ConfigMaps, Deployments ,StatefulSet manifests, PersistentVolumes and editable settings for them.
Why do we need Helm?
Managing repeating Kubernetes manifest or copying from one to another, editing hardcode values and validating syntax, sharing across env like Dev, QA, Production etc. is hard.
 MANAGE COMPLEXITY Charts describe even the most complex apps, provide repeatable application installation, and serve as a single point of authority. |
 EASY UPDATES Take the pain out of updates with in-place upgrades and custom hooks |
 SIMPLE SHARING Charts are easy to version, share, and host on public or private servers. |
 ROLLBACKS Use helm rollback to roll back to an older version of a release with ease. |
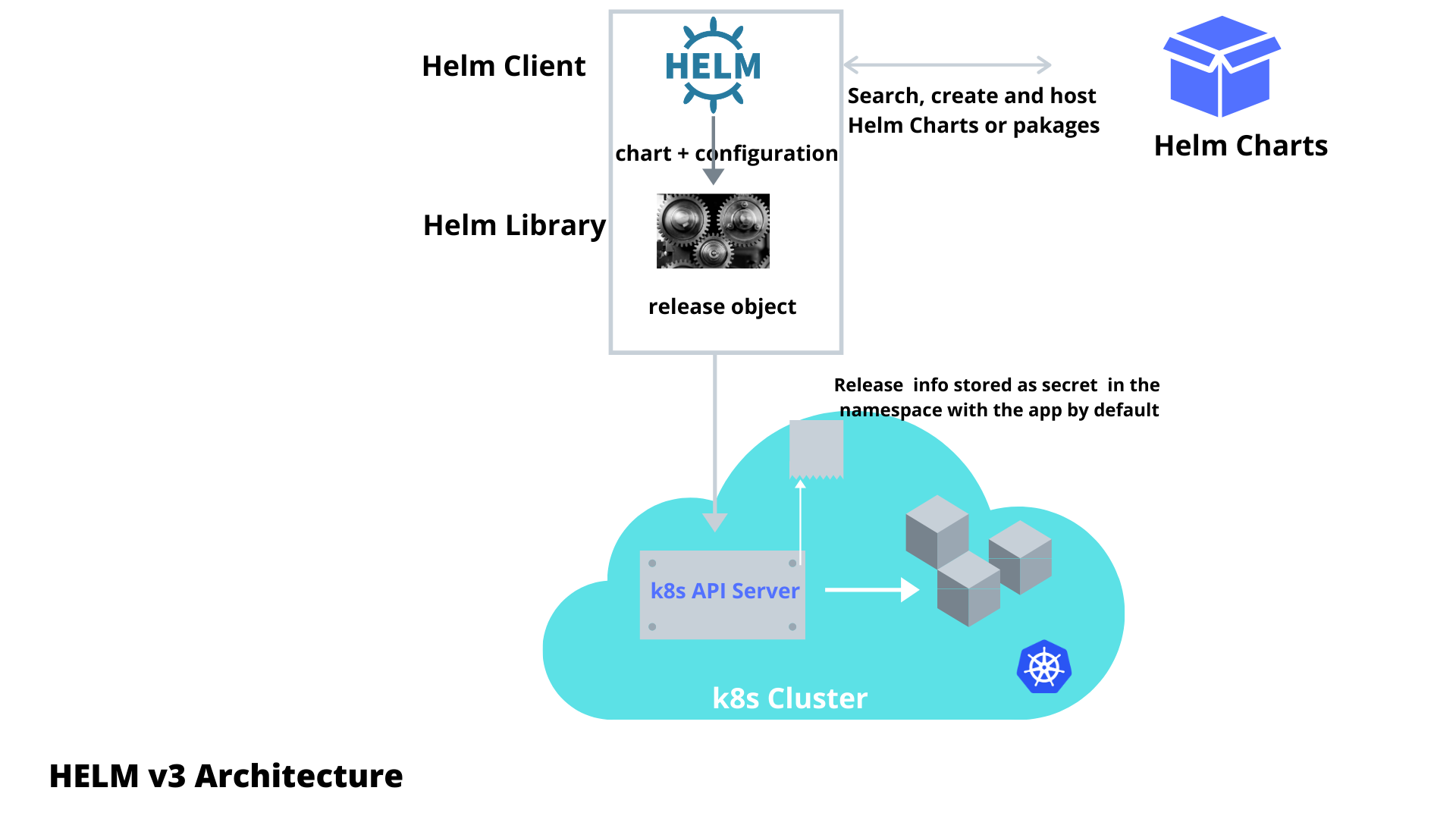
New Architecture of Helm 3
There are 3 important concepts for Helm
The chart is a bundle of information necessary to create an instance of a Kubernetes application.
The config contains config info to create a releasable object.
A release is a running instance of a chart, combined with a specific config.
COMPONENTS - The Helm SDK is implemented into two parts using golang
The Helm Client is a command-line client for end users. The client is responsible for
- Local chart development
- Managing repositories
- Managing releases
- Interfacing with the Helm library
- Sending charts to be installed
- Requesting upgrades or uninstalling of existing releases
The Helm Library provides the logic for executing Helm operations. It interfaces with the Kubernetes API server and provides the following capability:
- Combining a chart and configuration to build a release
- Installing charts into Kubernetes and providing the subsequent release object
- Upgrading and uninstalling charts by interacting with Kubernetes
Install Helm 3
you can install and use Helm for your choice of operation system, it comes for linux, macOs and Windows
Linux - Run the client installer script that Helm provides:
$ curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/master/scripts/get-helm-3 > get_helm.sh
$ chmod 700 get_helm.sh
$ ./get_helm.sh
macOS - Use Home brew to install:
$ brew install helm
Windows - Use Chocolatey to install:
$ choco install kubernetes-helm
$ helm version
version.BuildInfo{Version:"v3.1.1", GitCommit:"afe70585407b420d0097d07b21c47dc511525ac8", GitTreeState:"clean", GoVersion:"go1.13.8"}
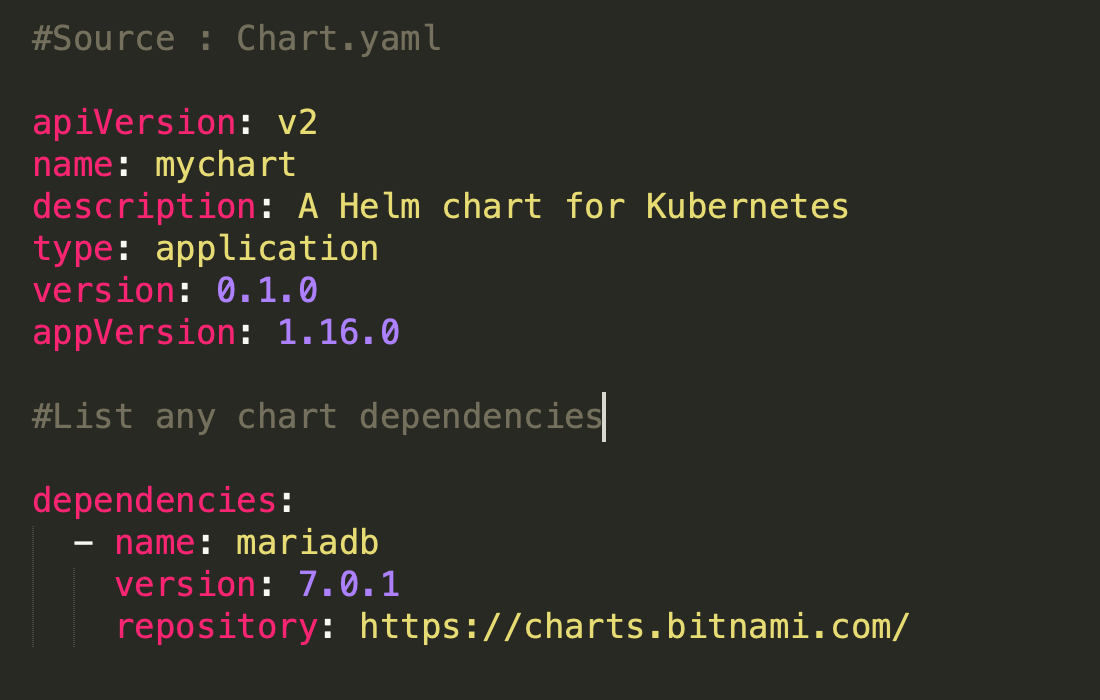
Helm chart directory structure looks like as follows

Chart.yaml keeps information about metadata of your current chart, version number and chart dependencies.
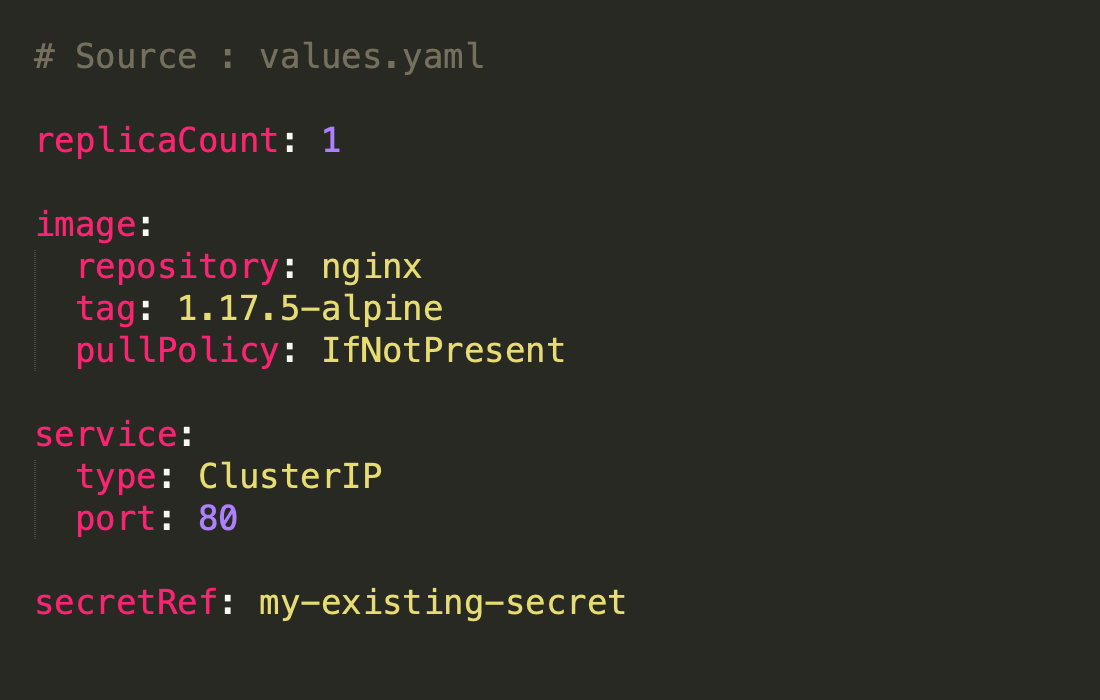
values.yaml values file contains a collection of key values that represent configuration settings for a chart.
Templates
Files under templates directory are treated as dynamic YAML files, these are implemented using the go template lang. you can have more detaile on Sprig Function Documentation
YAML templates prevents config duplication and allows you to install same charts in dev, staging or production environment.
Installing a Chart
1. From a Chart Directory
$ helm install myapp ./mychart
2. From a remote chart repo
$ helm install myapp myrepo/mychart
Using custom values
1. Using a values file
$ helm install myapp ./mychart -f my-values.yaml
2. Using a key value pair
$ helm install myapp ./mychart --set image.tag=master
3. Advanced use
$ helm install myapp ./mychart \
-f qa.yaml \
-f staging.yaml
References
More Info: https://helm.sh/
Read Doc: https://helm.sh/docs/
GitHub: https://github.com/helm/helm
HelmHub : https://hub.helm.sh/
Enjoyed this article? Share it.







