Kubernetes Services & Types
Kubernetes stands out as a powerful tool for managing, scaling, and deploying containerized applications. At the heart of Kubernetes lies its service management capabilities, which play a crucial role in facilitating communication between various components within a cluster. In this guide, we delve into Kubernetes services, exploring their types, functionalities, and best practices.
What is a Kubernetes Service?
In Kubernetes, a service is an abstraction layer that defines a logical set of pods and a policy by which to access them. It enables communication and discovery between different components of an application by providing a stable endpoint.
Types of Kubernetes Services
Kubernetes offers several types of services, each designed to fulfill specific requirements and use cases:
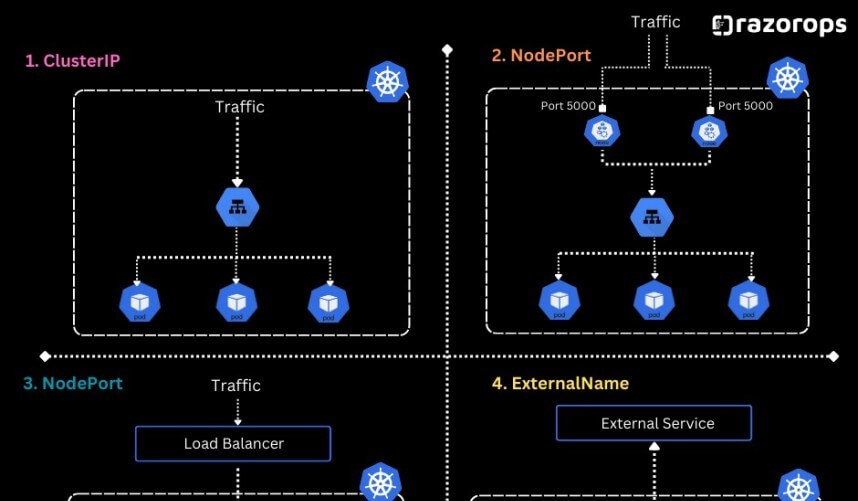
ClusterIP: A ClusterIP service exposes the service on an internal IP within the cluster.This type of service is accessible only from within the cluster, making it ideal for internal communication between components.ClusterIP services are not accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster.
NodePort: A NodePort service exposes the service on each node’s IP at a static port.This makes the service accessible from outside the Kubernetes cluster by accessing any node’s IP address and the specified port number.NodePort services are suitable for scenarios where external access is required, but they might not be optimal for production environments due to security concerns.
LoadBalancer: A LoadBalancer service automatically provisions an external load balancer from a cloud provider’s pool.It assigns a stable external IP address to the service, allowing access from outside the cluster.LoadBalancer services are commonly used in production environments to distribute traffic across multiple pods.
ExternalName: An ExternalName service maps the service to the contents of the externalName field.It enables the use of a service name in the cluster to refer to an external resource outside the cluster.This type of service is often used for integrating with external services or DNS names.
Best Practices for Kubernetes Services
To leverage Kubernetes services effectively, consider the following best practices:
Use Labels and Selectors: Labels and selectors are fundamental concepts in Kubernetes that allow services to target specific pods based on metadata. Utilize them consistently to ensure accurate pod selection by services.
Implement Service Discovery: Leverage Kubernetes’ built-in DNS for service discovery within the cluster. This allows services to communicate with each other using their assigned DNS names.
Secure Your Services: Depending on the service type, implement appropriate security measures such as Network Policies, Ingress controllers, or authentication mechanisms to safeguard your services from unauthorized access and potential security threats.
Monitor and Scale Accordingly: Monitor the performance and resource utilization of your services using Kubernetes monitoring tools. Scale your services horizontally or vertically based on demand to ensure optimal performance and resource allocation.
Regularly Update and Maintain Services: Keep your services up to date with the latest Kubernetes versions and patches to benefit from new features, bug fixes, and security enhancements. Regular maintenance ensures the stability and reliability of your applications.
Kubernetes services play a pivotal role in enabling seamless communication and connectivity within containerized applications. By understanding the different types of services available and adhering to best practices, organizations can effectively harness the power of Kubernetes to build scalable, resilient, and robust container-based solutions. Embrace Kubernetes services as a cornerstone of your container orchestration strategy and unlock the full potential of modern application deployment and management. Follow RazorOps Linkedin Page Razorops, Inc.
Enjoyed this article? Share it.







