What is Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery?
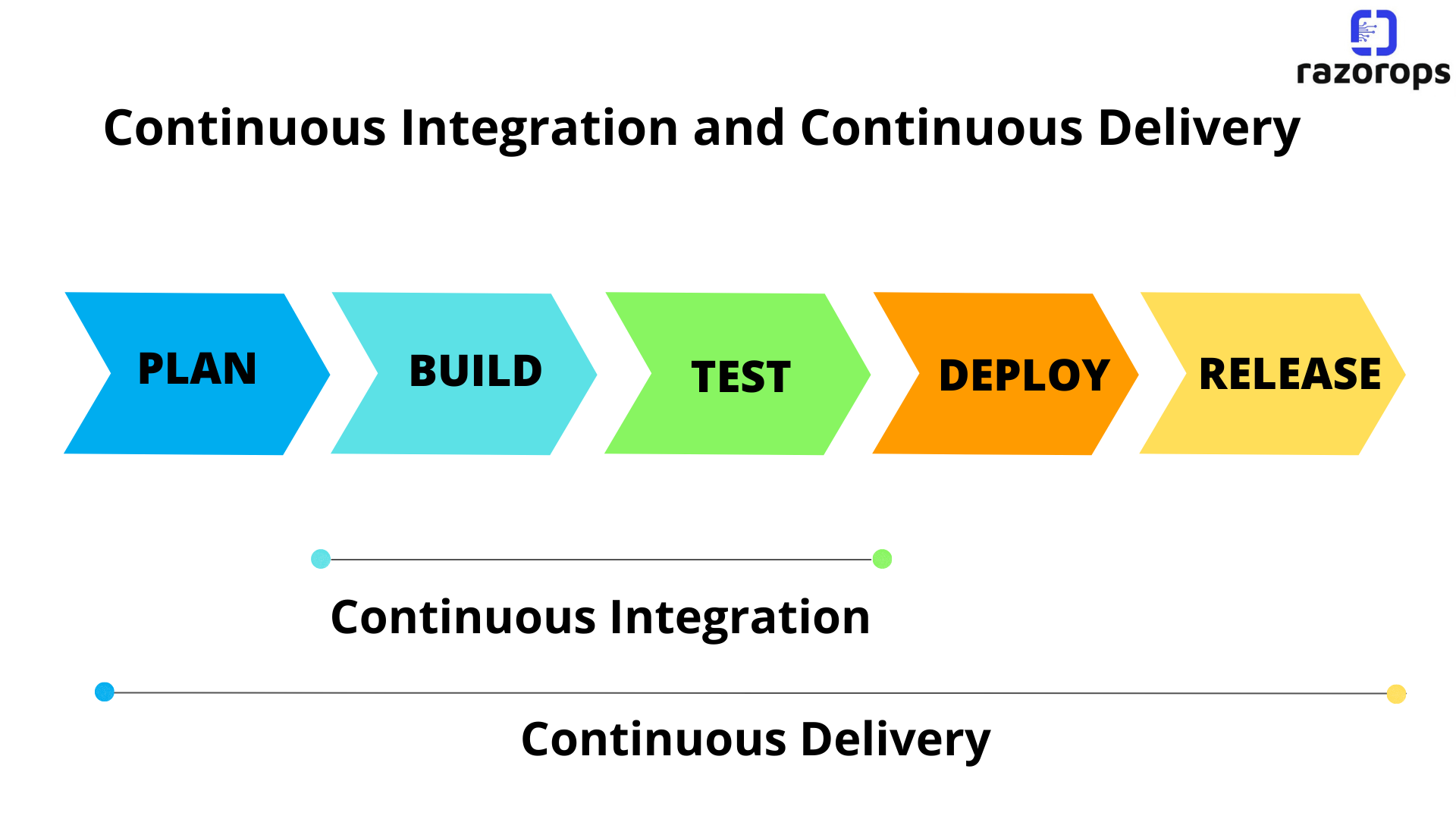
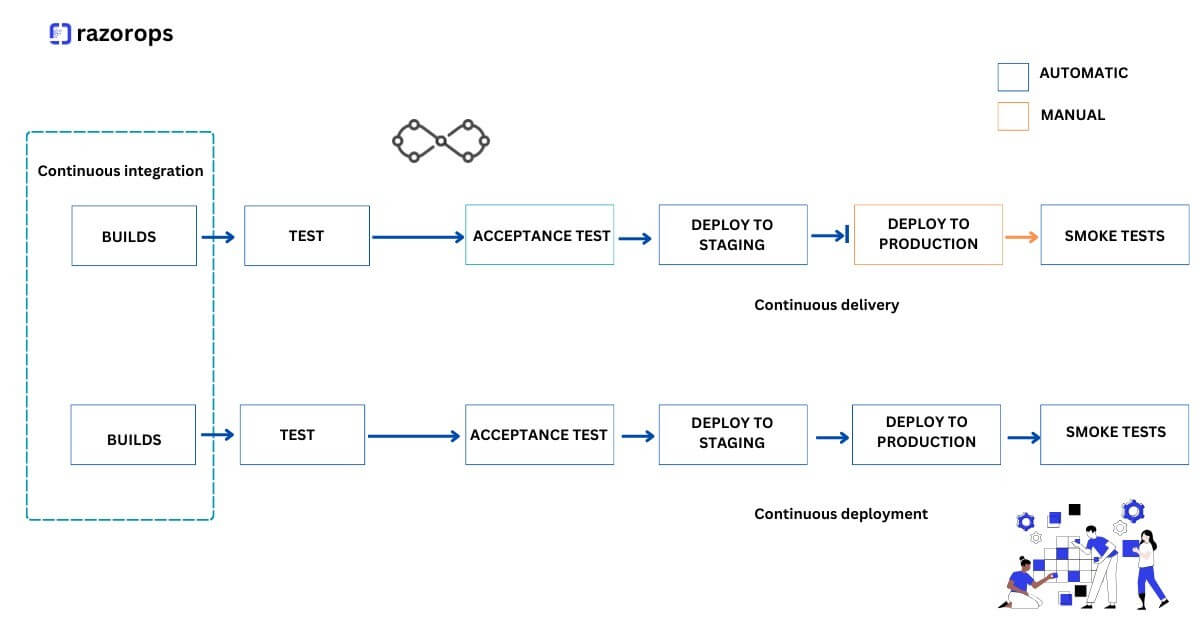
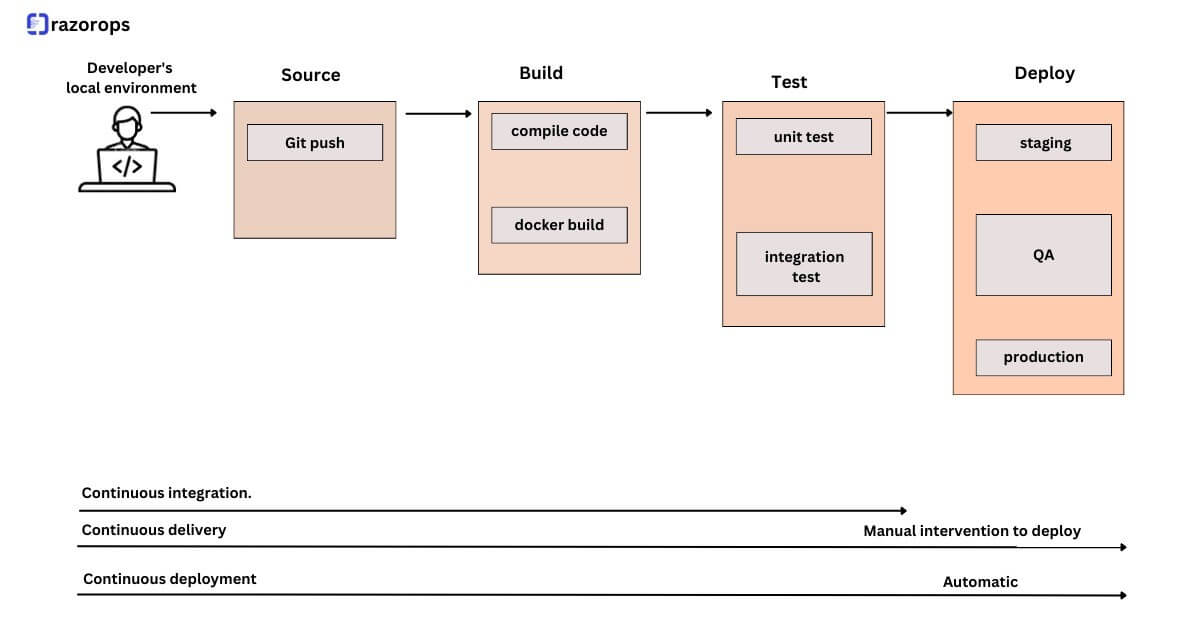
Continuous integration is a DevOps practice, where developers continuously integrate the code changes into a central repository. It most often refers to the build or the integration stage of the software release process. A continuous integration service helps to automatically build and run unit tests on the new code changes to find any errors instantly.
ADVANTAGES OF CONTINUOUS INTEGRATION:
- Helps you to increase the software quality
- It enables you to conduct repeatable testing.
- CI allows developers to work independently on different features in parallel.
- It can increase visibility
Continuous delivery expands upon continuous integration by deploying all the code changes to the testing environment and later to the production environment after the build stage. When correctly implemented,this will allow developers to always have a deployment-ready build that has passed all the standardized test processes. It will help the developers to closely validate the changes and discover any new issues. With continuous delivery, you can choose when to deploy like daily, weekly, fortnightly, or whatever best suits the business requirements.
The main difference between continuous delivery and continuous deployment is that continuous delivery needs the presence of a manual approval to update to production. With continuous deployment, production will happen automatically without any explicit approval.
ADVANTAGES OF CONTINUOUS DELIVERY:
- Automate the software release process which makes software delivery more efficient and quick
- It helps you to find bugs earlier in the delivery process.
- CD allows to deliver updates immediately and frequently to clients/customers
Let’s check: What is CI/CD Pipeline & How its Works

Continuous integration and Continuous Delivery Benefits:
- Version Control: Version control makes it easy to collaborate with a team and also helps in maintaining visibility in the progress of the software.
-
Process Automation: Helps to automate the build process
- Fault isolation: Automated testing and the monitoring systems makes the use of mechanisms to identify when a bug is identified and it pinpoints the location.
- Mean Time To Resolution (MTTR): It helps to track how quick a broken feature has been fixed.
- Quicker Release: With fault isolation and MTTR the defects are fixed in the early stage which makes the deployment also faster.
- Decreased risk : With automated regression and unit testing we can identify the bugs faster .
- Collaborations: Helps multiple teams to work with others more efficiently.
- Increased customer satisfaction: With frequent feature release and minimum bugs increase the customer satisfaction.
Conclusion:
Continuous Integration makes the software release process easier with automated processes to build, test and deploy
Continuous Delivery collects the code stored in the shared repository and continuously delivers it to the production environment.
Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery increases the software quality and provides a bug free environment to the user.