What is CICD Pipeline? Explanation of CICD Pipeline along with Examples.
WHAT IS CI/CD?
Continuous Integration(CI) is a software development practice where developers frequently merge the code and the changes in a central repository. The important goals of continuous integration is to find and resolve the bugs more quicker, improve the software quality, and reduce the time taken to validate and release new software updates. Continuous Delivery(CD), which is done on the top of Continuous Integration and includes the practice of automating the entire software release process and builds.
WHAT IS CI/CD PIPELINE?
CI/CD pipeline is a series of steps that include all the stages from the beginning of the CI/CD process and it is responsible for creating an automated and seamless software delivery process. With a CI/CD pipeline, a software release artifact can move and progress through the pipeline right from the code check-in stage through the builds, tests, and different deployment stages.
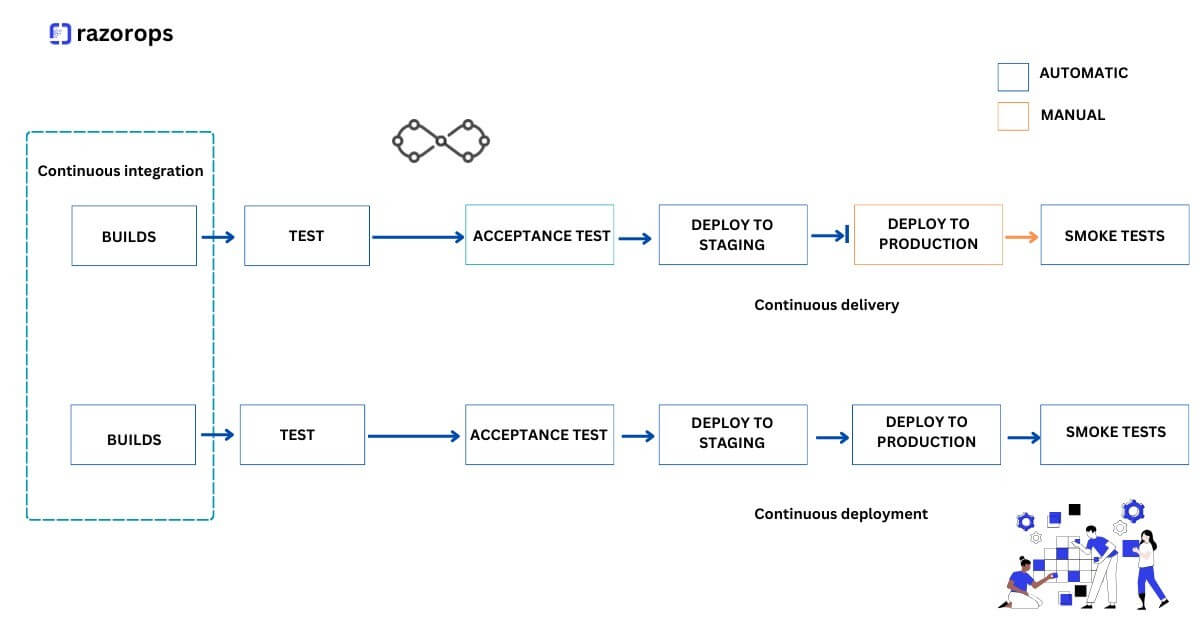
A CI/CD pipeline consists of a series of sub-processes that can be classified into two major categories – Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery.
- Continuous Integration: Plan, Code, Build and Test stages/scenarios
- Continuous Delivery: Test, Release, Deploy and Operate.
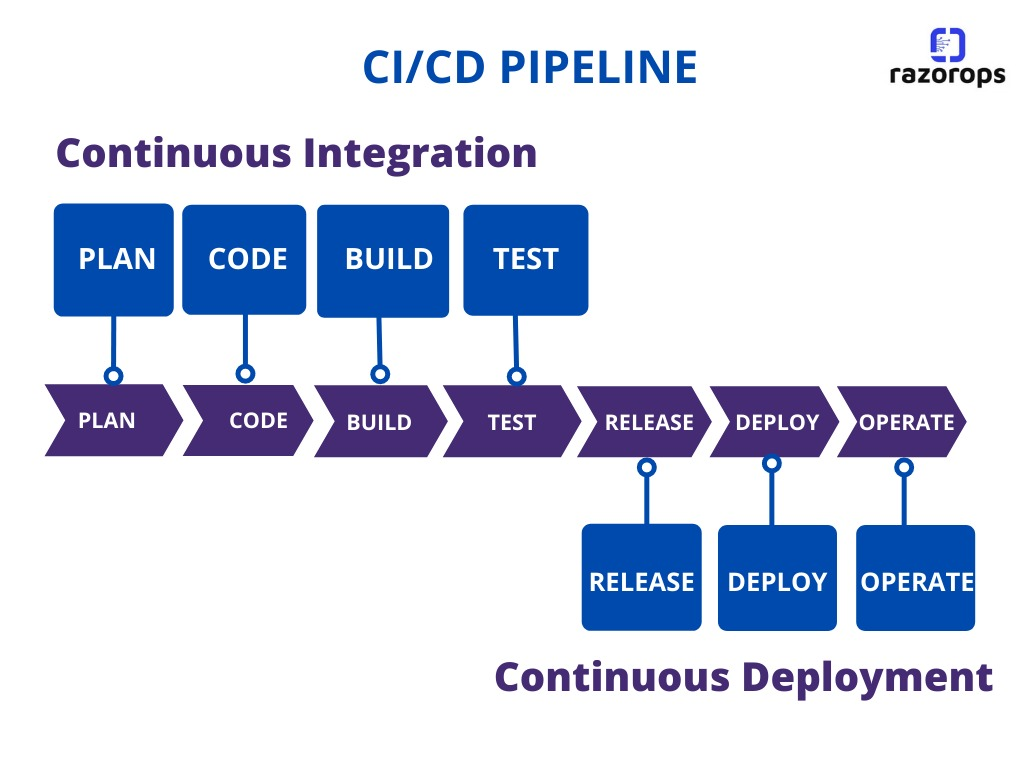
Let’s Check : Continuous Integration vs Continuous Deployment vs Continuous Delivery
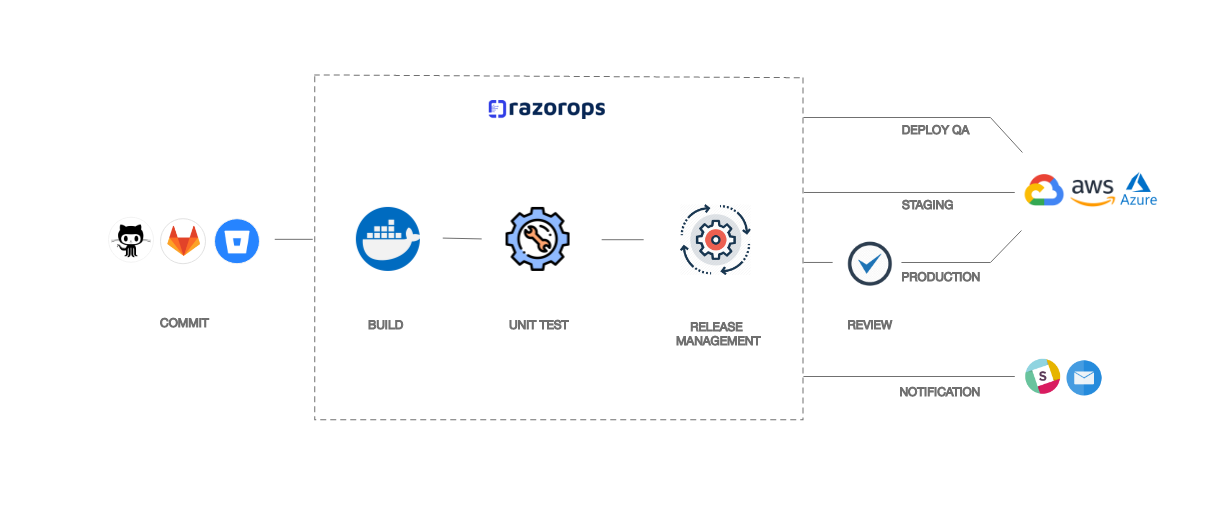
Pipeline stages :
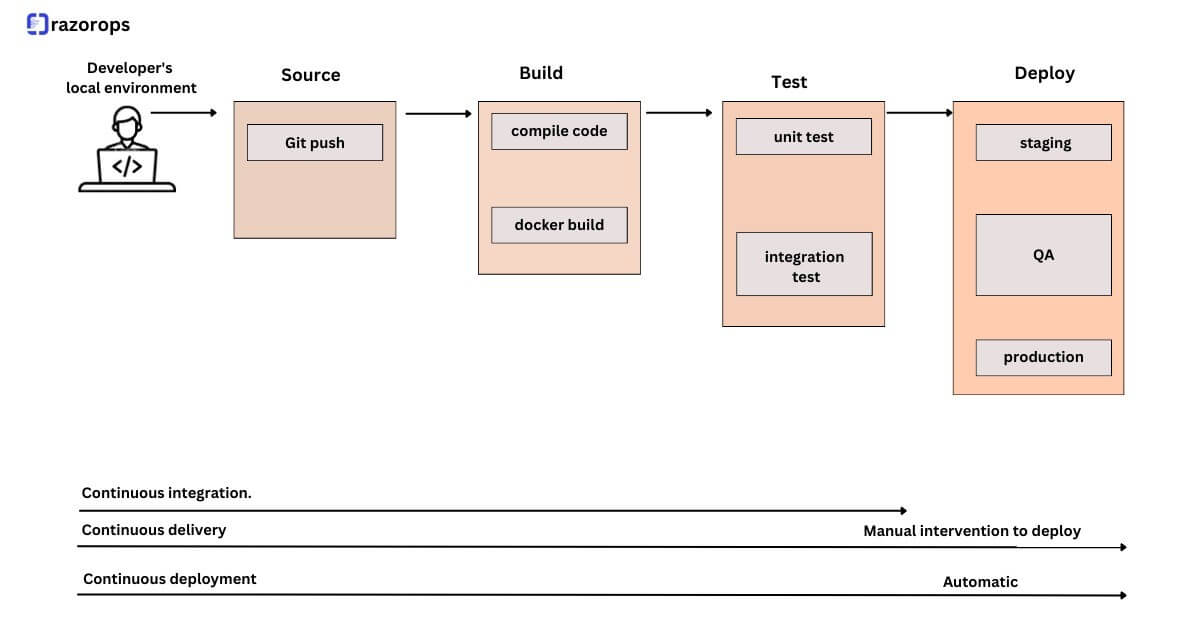
A CI/CD pipeline can be classified further into four main stages:
- Source
- Build
- Test
- Deployment
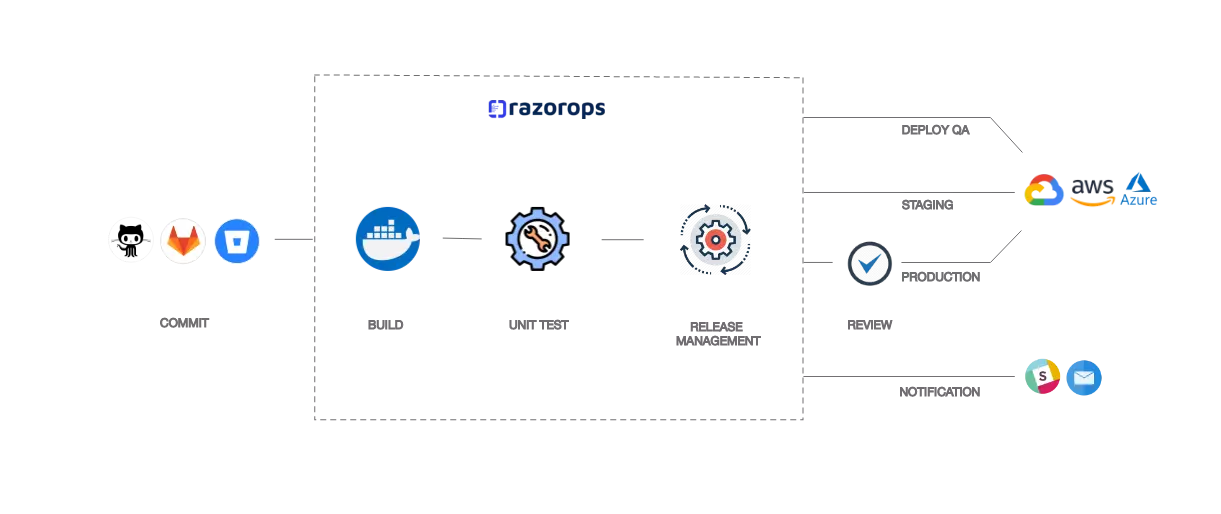
1. Source: An organization stores application codes in a centralized repository system to carry the versioning, tracking changes, collaborating, and auditing, as well as to ensure security and maintain control of the source code. We can consider it the baseline unit of the CI phase.
2. Build: This is the most important stage of application development, and when this is completely automated, it allows the developer team to test and build their release multiple times a day. The build artifacts can be stored into an artifact repository and then deployed to the environments.The main advantage of using an artifact repository is that they make it possible to go back to a previous version of the build, if that’s ever necessary.
3. Testing: Automated tests play a crucial role in any application development-deployment cycle. The automated tests can be broken down into three categories:
-
Unit test: Developers divide an application into smaller units of code to perform testing. This test should always be a part of the build process and can be automated.
-
Integration test: In the world of microservices to allocate applications, it is important that all components work as expected when multiple modules of an application are integrated. This stage may require testing of APIs, integration with a database, or other services. This test is generally part of the deployment and the release process.
-
Functional test: This is end-to-end testing of application or product, generally performed on staging servers as part of the release process.
Know more: Unit Test vs Integration Test
4. Deployment: Once the build is completed and the automated tests for the release are completed, the last stage of the pipeline is to automate deployment of the new code to the next environment in the pipeline. In this stage, the tested code is deployed to the production environment.There are different types of deployment strategies such as blue-green deployment, canary deployment, and in-place deployment for deploying on a production environment:
- In a blue-green deployment, there will be multiple production environments running parallel. The new “green” version of the application or service is accounted for in parallel with the last stable “blue” version running on a distinct infrastructure. Once your green is tested and ready, the blue can be revoked.
- In a canary deployment, the deployment is done to lesser nodes first and, after it is tested using those nodes, and then it will be deployed to all the nodes.
- In-place deployment deploys the code directly to all the live nodes and might suffer downtime; however, with rolling updates, you can reduce or remove downtime.
Benefits of CI/CD:
- Automated testing allows continuous delivery processes to keep checks of software quality and security, and increases the profitability of code in production.
- CI/CD pipelines allow a much shorter time to market for the new product features, make customers happier and lower strain on development.
- The rapid increase in inclusive speed of delivery which is enabled by CI/CD pipelines to improve an organization’s competitive edge.
- Automation allows team members to focus on what they have to do, which increases the best end products.
CONCLUSION:
A CI/CD pipeline automates the software delivery process. The pipeline builds the code, runs tests (CI), and safely deploys a new version of the application (CD). Automated pipelines will help to remove manual errors, provide systematized feedback loops to developers, and enable fast product iterations and deliverability . Razorops is a CI/CD platform which helps to be 100% operational on a technical level so we can focus on delivering the best product in a short amount of time.With Razorops,there will be very little overhead and