
CI/CD Pipelines Streamlining Software Delivery with Automation
Software development landscape, efficiency is key. One of the most effective ways to achieve this is through Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. These automated pipelines streamline the process of building, testing, and deploying software, enabling teams to deliver high-quality code at scale with speed and precision.
Understanding CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines are the backbone of modern software development workflows. They automate the steps involved in delivering software, from integrating code changes to deploying them into production environments. Let’s break down the key components:
Continuous Integration (CI): This involves automatically building and testing code changes as soon as they are committed to the version control repository. CI ensures that all changes are integrated smoothly, helping to identify and address issues early in the development cycle.
Continuous Delivery (CD): Once code changes pass the CI phase, they are automatically deployed to staging or pre-production environments for further testing. CD ensures that software is always in a deployable state, ready to be released to customers at any time.
What are CI, CD, and continuous deployment?
As previously stated, the CI/CD pipeline incorporates both continuous integration and continuous delivery to create a more-encompassing software development culture and set of operating principles. But what exactly are CI and CD, and how do they relate to continuous deployment?
What is continuous integration (CI)?
Continuous Integration (CI) is an approach in which development teams regularly implement and test incremental changes to the code. These changes are then merged to a shared, central repository. The repository is version controlled, allowing developers to view updates and go back to earlier versions when necessary. These iterations, called ‘check ins’ can occur multiple times per day during the development cycle. Every change is verified by an automated build and tests to ensure that issues in the code may be quickly identified and resolved.
What is continuous delivery (CD)?
While CI automates development and testing, Continuous Delivery (CD) closes the cycle, by automating aspects of software delivery. As feedback is addressed and fixes are implemented, these changes are automatically uploaded until the team makes the decision to push the application to production. CD results in a deployable product but depends on human authorization to roll out products, allowing teams to decide what should be released and when. This enables developers to continue to refine the application before handing it over to the end user.
What is continuous deployment?
Continuous deployment is similar to continuous delivery, so much so that they are sometimes used interchangeably and represented by the same abbreviation (CD). The major difference between continuous deployment is in who actually deploys the software. Instead of requiring human authorization to release a product, continuous deployment sends every change through an automated pipeline to create a working version, which is then pushed immediately into production. There is no holding for a manual approval cycle, which means that the code itself must be sufficiently tested prior to entering production.
What are the steps to a CI/CD pipeline?
CI/CD is as much a cultural shift as a procedural one. As such, the specific steps in a CI/CD may vary from organization to organization. That said, they tend to follow a basic, uniform structure
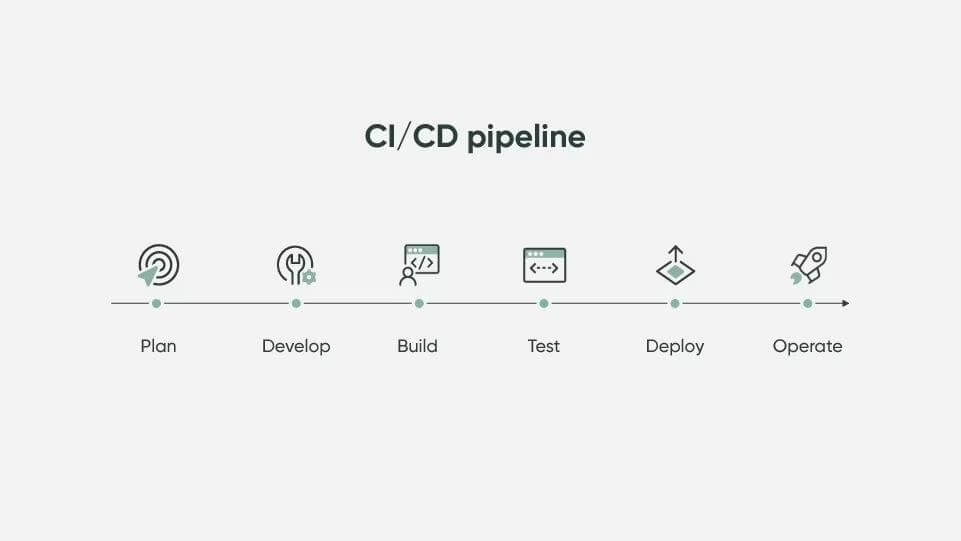
Plan
The first stage of the CI/CD pipeline includes all the background legwork that goes into conceptualizing a new application. Project/product managers gather requirements from customers and stakeholders, build a project roadmap, and create a backlog of necessary tasks. This stage also includes incorporating Agile management tools CI/CD pipeline
Develop
The development stage relies on simplified coding (a key principle of Agile) and fast feedback. Using continuous development principles, and including security early in the process, code is constantly validated to ensure its correctness.
Build
Continuing from development, the build stage relies on teams working in short iterations to create runnable instances of the product. Any issues that prevent a product from passing the build stage must be addressed immediately.
Test
This stage employs automated tests to ensure that the code is functioning as intended. The test phase should weed out any bugs from reaching the customer, and quickly produce developer feedback to help them isolate and remediate issues before they can grow into real problems. More mature CI/CD pipeline testing may extend into scanning for security vulnerabilities, something often referred to as DevSecOps.
Deploy
With test-validated code, the project can now be sent to a deploy environment. These are usually staging environments where the code may be subjected to additional manual testing and review, with approved changes automatically sent to production.
Operate
Once deployed and sent into production, the application is closely monitored to identify trends and potential problems. This is often integrated within the operational capabilities of the application and informs future updates.
Benefits of CI/CD Pipelines
Implementing CI/CD pipelines offers numerous benefits for software development teams
Faster Time to Market: Automation reduces manual overhead and accelerates the delivery process, allowing teams to release new features and updates more frequently.
-
Improved Quality: Automated testing catches bugs and regressions early, ensuring that only high-quality code is deployed into production environments.
-
Reduced Risk: With automated builds, tests, and deployments, the risk of human error is significantly reduced, leading to more reliable software releases.
-
Increased Collaboration: CI/CD encourages collaboration among team members by providing visibility into the entire development process and fostering a culture of transparency and accountability.
Implementing CI/CD Pipelines
To implement CI/CD pipelines effectively, follow these best practices:
Start Small: Begin by automating the most critical and time-consuming tasks, such as building and testing code changes. As your team becomes more comfortable with the process, gradually expand the scope of automation.
-
Standardize Environments: Ensure consistency across development, testing, and production environments to minimize compatibility issues and deployment failures.
-
Monitor and Iterate: Continuously monitor the performance of your CI/CD pipelines and gather feedback from stakeholders to identify areas for improvement. Iterate on your processes to optimize efficiency and reliability.
-
Embrace DevOps Culture: CI/CD is not just about tools and technology—it’s also about fostering a culture of collaboration, communication, and continuous improvement across development and operations teams.
CI/CD pipelines are a game-changer for software development, enabling teams to deliver value to customers faster, more reliably, and with higher quality. By automating repetitive tasks and streamlining the delivery process, CI/CD empowers teams to focus on innovation and creativity, driving business success.
Tutorials & Guides
Top Reading Recommendations
Upcoming Events
Cloud Native Thane X Grafana Meetup
March 9 , 10:00 AM – 2 :00 PM (PST)
Brew Meet - The IoT Around Us
March 9, 11:30 AM – 2 :30 PM (PST)
Docker Masterclass
March 10, 10 :00 - 11:30 AM (PST)
DevOps Jobs
Google - Check out all the jobs
here
Accenture -Check out all the jobs here
Infosys -Check out all the jobs here
Microsoft -Check out all the jobs
here

PS- We publish this newsletters every week, Subscribe and share with your friends. We hope this newsletter has provided valuable information. Follow RazorOps Linkedin Page Razorops, Inc.




